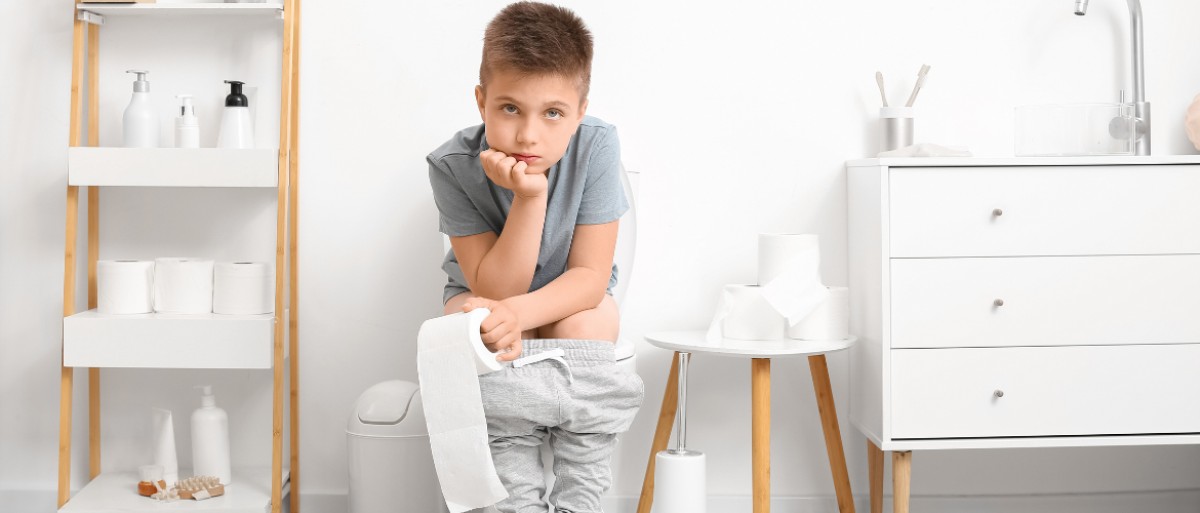
What is diarrhea?
Η
diarrhea is a common problem characterized by
frequent, watery bowel movements;. It may be temporary or a sign of a more serious condition. Understanding the causes, symptoms and prevention methods can help manage this unpleasant condition.
Symptoms of Diarrhea
The
symptoms of diarrhea may include:
- Inflation
- Motion sickness
- Urgent need to void
- Vomiting
- Cramping or abdominal pain.
- Fever
- Blood in the stool
- Dehydration
Η
dehydration often occurs after diarrhea, and can be life-threatening if left untreated. Dehydration is especially dangerous in children, older adults and people with weakened immune systems
immune system.
Symptoms of dehydration in adults
- Excessive thirst
- Dry mouth or skin
- Little or no urination
- Weakness, dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fatigue
- Dark urine
Symptoms of dehydration in children
- Dry mouth and tongue
- Crying without tears
- Fever above 39 C
- Drowsiness, unresponsiveness or irritability
What causes diarrhea?
The
causes of diarrhea they can be many and varied, including:
- Viruses: Such as Norwalk virus (also known as norovirus), enteric adenoviruses, astervirus, cytomegalovirus and hepatitis virus. Rotavirus is a common cause of acute diarrhea in children.
- Bacteria and parasites: Exposure to certain bacteria, such as E. coli or parasites through contaminated food or water, leads to diarrhea.
- Other digestive disorders: Such as IBS, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, microscopic colitis and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO).
- Medicines: Many medications, such as antibiotics, can cause diarrhea.
- Lactose intolerance: People who have trouble digesting lactose have diarrhea after consuming dairy products. Lactose intolerance can increase with age because levels of the enzyme that helps digest lactose drop as you get older.
- Surgical procedures: Certain surgeries, such as removing part of the intestine or gallbladder, can cause diarrhea.
Diet when I have diarrhea
The
foods which we should consume when we have
diarrhea are the folowing:
- Bananas
- Rice
- Boiled vegetables
- Oatmeal
- Dry cereals
- Boiled potatoes or roasted (peeled)
- Chicken in the oven without skin
What stops diarrhea
Most cases of acute diarrhea are effectively treated without specific treatment. However, if the diarrhea is caused by bacteria or parasites, antibiotic medication may be needed. Hydration is critical, and adults are advised to drink plenty of fluids
electrolytes, juices or broths. For children, using electrolyte replacement serums can help prevent dehydration or replace lost fluids.
A change in diet can also
stop diarrhea. It is recommended to avoid dairy, high fat, high fiber or highly spiced foods for a few days.
If the diarrhea continues for more than two days without improvement, is accompanied by severe abdominal pain or fever, or blood appears in the stool, it is important to see a medical professional for further evaluation and treatment.
Prevention of Diarrhea
For the
prevention of diarrhea, it is important to follow good hygiene practices, such as:
- Frequent hand washing: Especially before and after preparing food, after using the toilet, and after handling food such as uncooked meat.
- Proper food processing and storage: Ensure food is cooked and stored properly.
- Hand washing time: Wash and rub your hands together thoroughly for at least 20 seconds.
- Hand disinfectant: When you can't wash your hands in a sink use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
When you travel:
Prefer hot and well-cooked foods. Avoid raw fruits and vegetables unless you can clean them yourself. Avoid raw or undercooked meats and dairy products. Only drink bottled beverages such as water, soda, beer, or wine from their original container. Do not drink tap water or use ice cubes. Use bottled water to brush your teeth. Drinks made with boiled water such as coffee and tea are usually safe. Remember, alcohol and caffeine can cause diarrhea and dehydration.
When to see a doctor
If you are an adult, see your doctor if:
- You have diarrhea for more than two days without improvement
- You have become dehydrated
- You have severe pain in the abdomen
- You have bloody stools
- You have fever above 39 C
Η
diarrhea it can be an unpleasant experience, but with proper management and care, most cases are successfully treated. Prevention through good hygiene practices and the implementation of simple self-care measures can significantly reduce the risk of occurrence or the intensity of diarrhea. In case of severe or persistent symptoms, a visit to the doctor is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Related products at
wecare.gr
Sources:
1)
Diarrhea - Symptoms and causes2)
What causes diarrhea?3)
Diarrhea Symptoms 4)
Can diarrhea be prevented? 5)
What you should know about diarrhea 6)
Symptoms & Causes of Diarrhea
PHARMACIST, M.Sc.
CEO Wecare IKE