Ο
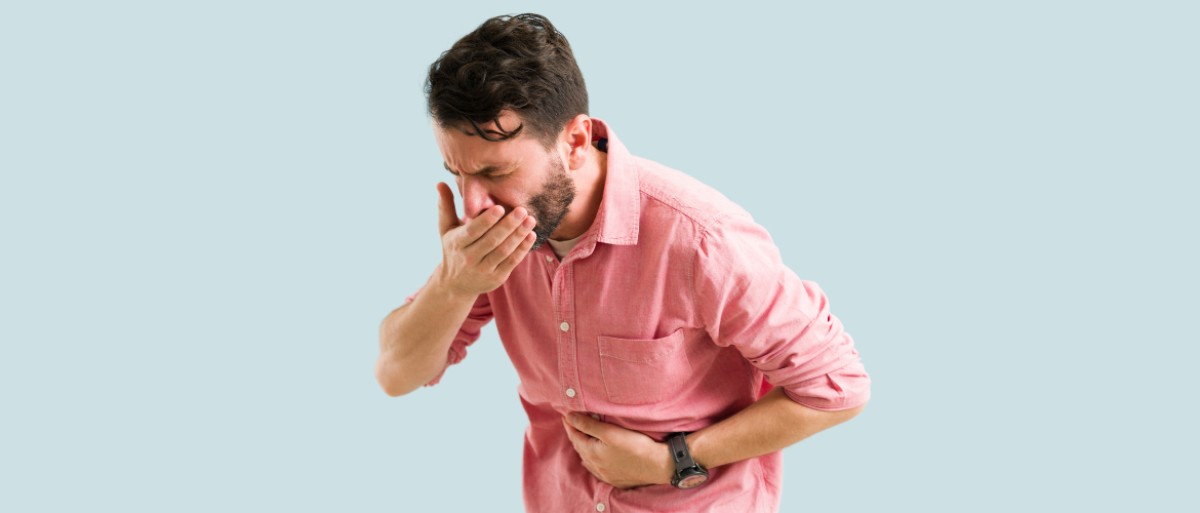
stomach pain high in the center it is often due to problems such as reflux, gastritis or indigestion. However, it can also be a sign of more serious conditions, such as inflammation of the gallbladder, pancreatitis or heart attack. Usually, this pain is not a cause for concern and may be accompanied by heartburn, nausea, vomiting, gas, bloating or diarrhea. If the pain is very intense, does not subside in a few hours, or other symptoms such as shortness of breath, dizziness, chest tightness or fainting appear, you should see a specialist immediately.
What causes upper center stomach pain?
Pain high in the center of the stomach it can be due to various causes. To find out what exactly is causing the pain, you should see a doctor for an evaluation. These are some of the most common causes of upper stomach pain:
1. Gastritis
Η
gastritis is a condition where the inside of the stomach is inflamed, often causing pain in the upper part of the stomach,
burning or tightness, especially after eating. Other symptoms include;
- Motion sickness
- Feeling of satiety
- Belching
- Excessive gas
- Puke, who can bring relief
Causes of gastritis include eating an unhealthy diet of fried foods, stress, frequent use of anti-inflammatory medications, and infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
Treatment of gastritis includes medicines prescribed by a gastroenterologist such as omeprazole to reduce stomach acid and, in case of infection, antibiotics such as clarithromycin or amoxicillin. It is also important to change eating habits, such as avoiding alcohol and spicy foods.
2. Esophagitis
Η
esophagitis is an inflammation of the esophagus, usually caused by acid reflux from the stomach or due to a hiatal hernia. This condition can cause burning in the chest and stomach pain, especially after eating. The pain may be worse at night and is not relieved by rest. Alcohol, caffeine and fried foods can make symptoms worse.
The doctor often prescribes drugs that reduce stomach acidity. Lifestyle changes such as stopping smoking and avoiding alcohol, fat and ready meals are also recommended. In severe cases, surgery may be needed to improve symptoms and prevent reflux.
3. Dyspepsia
Η
indigestion is the difficulty in digesting food and can be caused by several reasons:
- Eating too much quantities food.
- Consumption of foods that does not tolerate good your organization.
- Eating foods that are contaminated with bacteria or other microorganisms.
- Consuming foods containing them lactose.
These conditions can cause symptoms such as:
- Increased gas production
- Regression
- Increased bowel movement
- Diarrhea
- Inflation
- Constipation
These symptoms may include upper stomach pain or more general abdominal pain.
Usually, the pain subsides after a few hours. For relief it is good to drink
quite liquid and to prefer
light meals. Prefer foods that do not irritate the stomach.
4. Acute pancreatitis
Η
pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas, which is located in the middle of the abdomen and helps digest food and produce hormones. This condition can cause
- Sudden and severe pain
- Puke
- Inflation
- Constipation
Η
Acute pancreatitis is a medical emergency that needs immediate medical attention to prevent further inflammation. Initially, doctors recommend fasting, intravenous hydration, and pain medication. In cases of infection, antibiotics may be given while in more severe cases, surgery may be required.
5. Gastroenteritis
Η
gastroenteritis is an inflammatory condition of the stomach and intestines. It is usually caused by viruses or bacteria. The main symptoms include;
- Pain in the abdomen
- Motion sickness
- Diarrhea
This condition often results from
eating contaminated food. Symptoms may appear shortly after eating a meal containing the microorganisms.
If you are experiencing symptoms of gastroenteritis, it is important to see a doctor. Treatment may include rest, plenty of fluids, and a diet of easily digestible foods. Learn what is safe to eat and what to avoid during this condition.
Treatment of stomach pain high in the center
The following general treatment steps are envisaged
of stomach pain high in the center, but you should consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment:
- Avoid irritating foods: Limit the consumption of foods and drinks that irritate the stomach, such as coffee, alcohol, spicy foods, and foods with high levels of fat.
- Medicines: Antacids or other medicines that reduce stomach acidity can help, such as omeprazole or ranitidine. Talk to your doctor about the appropriateness and dosage of such medications.
- Eat small and frequent meals: Prefer smaller and more frequent meals instead of large and heavy ones, so as not to overload the stomach.
- Stay hydrated: Good hydration is important, especially if the pain is accompanied by vomiting or diarrhea.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol: Smoking and alcohol can further irritate the stomach.
If the pain is severe, continues for several days, or is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, vomiting, difficulty swallowing, or black or bloody stools, it is important to see a doctor for further evaluation.
Related Products: