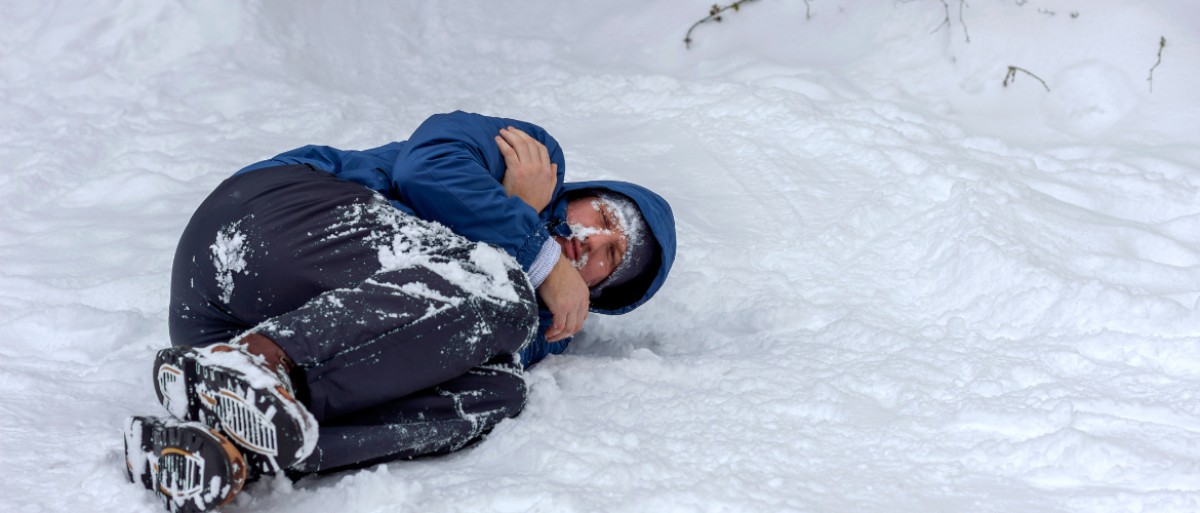
What is hypothermia?
Η
hypothermia is a critical health condition that occurs when the body's heat production cannot cover heat loss, leading to a dangerously low body temperature. A healthy body temperature is normally around 36 to 37 °C. However, when it decreases
below 35 °C, hypothermia occurs.
This decrease in body temperature can significantly disrupt the functioning of critical organs, such as the
καρδιά and
nervous system. Without immediate medical intervention, hypothermia can lead to serious complications, such as
heart failure and the respiratory system, and ultimately death.
One of the most common causes of hypothermia is
exposure to cold weather. To treat it, the central goal is to restore the body temperature to normal levels through various heating methods.
Symptoms of hypothermia
When the temperature starts to drop the first thing you will feel is the
shudder as it is considered as our organism's automatic defense against low temperature. Generally the
symptoms of hypothermia separated in
3 stages depending on the severity of the situation and are:
Mild hypothermia
Mild hypothermia means your body temperature is between
35°C and 32°C. The
symptoms of mild hypothermia include:
- Teeth that shake and grind.
- Exhaustion
- Clumsiness, slow movements and reactions.
- Drowsiness
- Weak pulse
- Fast heart rate (tachycardia)
- Confusion and poor judgment/loss of awareness
- Excessive urination
- Trouble speaking
- Fast breathing
- Pale skin color
- Confusion
Moderate hypothermia
Η
moderate hypothermia means your body temperature is between
32°C and 28°C. The
symptoms of moderate hypothermia include:
- Less shivering
- Speech is slurred
- Decreased mental function
- Difficulty thinking
- Hallucinations
- Blue skin color (cyanosis)
- Increased muscle stiffness.
- Dilated pupils
- Abnormal heart rhythm
- Decreased blood pressure
- Impaired reflexes
- Loss of conscience
- Slowing of breathing and heart rate
Severe hypothermia
Η
severe hypothermia means your body temperature is less than 28°C. The
symptoms of severe hypothermia include:
- Loss of chills
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Absence of reflexes
- Complete muscle stiffness
- Low urine production (oliguria)
- Fluid in the lungs
- The heart stops beating (cardiac arrest)
- Coma
- Death
Causes of hypothermia
The
causes of hypothermia they can be many and are usually related to the environmental conditions and the behavior of the individual. Some of the main causes include:
- Exposure to low temperatures: Staying in an environment with low temperatures without adequate protection from the cold is a common factor that can lead to hypothermia.
- Humidity and rain: The dangerous combination of low temperature with humidity or rain can increase the risk of hypothermia, as clothing becomes wet and loses its ability to retain heat.
- Heat Exchange: Heat is transferred directly from one object to another. For example, if you splash cold water on your face, you feel cooler because the heat from your body is transferred to the water.
- Inappropriate Attire: Choosing inappropriate clothing for the conditions can exacerbate the risk of hypothermia.
- Excessive exposure to cold: Staying in a cold environment for too long without heating can deplete the body's heat reserves.
It is important to take precautions when in a cold environment to avoid it
hypothermia, such as wearing appropriate clothing, being aware of humidity and seeking shelter and warmth when necessary.
Which people get hypothermia more easily?
The
people at increased risk of hypothermia is:
- Elderly
- Babies
- Children
- Homeless people
- People with mental illness
- People who are in outdoors for a long period of time
- People who do activities in the cold weather without proper equipment
I have hypothermia, what should I do?
- Remove any wet clothes
- Take the person's temperature if available thermometer
- Offer warm fluids (like soup or hot chocolate), but avoid alcohol and caffeine , which make the blood cool faster
- Do not give fluids to unconscious man
- Protect the person from the cold with some blanket or dry clothes
- Try to warm the person up with your own heat if there is no other solution
- Move quickly to one warm and dry place
Medical care
If the
hypothermia is in an advanced stage you should search
medical-hospital care to raise your body temperature properly. Treatment of hypothermia includes:
- Heating through passive methods: Use blankets to cover the person and provide hot drinks.
- Refreshing blood temperature: Heating the blood through a dialysis machine (usually used to clean the blood in patients with kidney problems) and recirculating it in the body.
- Warming through intravenous fluids: Injecting a warmed solution through an IV into a vein.
- Airway temperature refresh: Use of liquefied oxygen via mask or nasal cannula.
Can hypothermia be prevented?
When we are in a very cold situation we should always take the necessary measures to stay protected without hypothermia problems. The
elderly and the children they should be especially careful about it
prevention of hypothermia. Some
measures to prevent hypothermia which you should consider are the following:
- Dress in plenty of warm clothes.
- Eat and drink hot food and drinks.
- Wear suitable outdoor clothing such as scarf, gloves, cap, hats.
- Move when you feel cold to raise your body temperature.
- Avoid substances known to contribute to hypothermia, such as alcohol or certain drugs.
- Keep your home temperature above 20°C
When should I see my doctor?
Η
hypothermia is a condition that requires immediate attention. It is important to ask
medical attention immediately if you or someone you know shows symptoms of hypothermia. If not treated with treatment, the
hypothermia can develop into a critical situation.
Find on
wecare.gr the right vitamins you need!
Sources:
1)
Hypothermia - Symptoms and causes2)
Hypothermia: Signs, Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment3)
What is hypothermia?4)
Hypothermia (Low Body Temperature)5)
Hypothermia Treatment
PHARMACIST, M.Sc.
CEO Wecare IKE