Ο
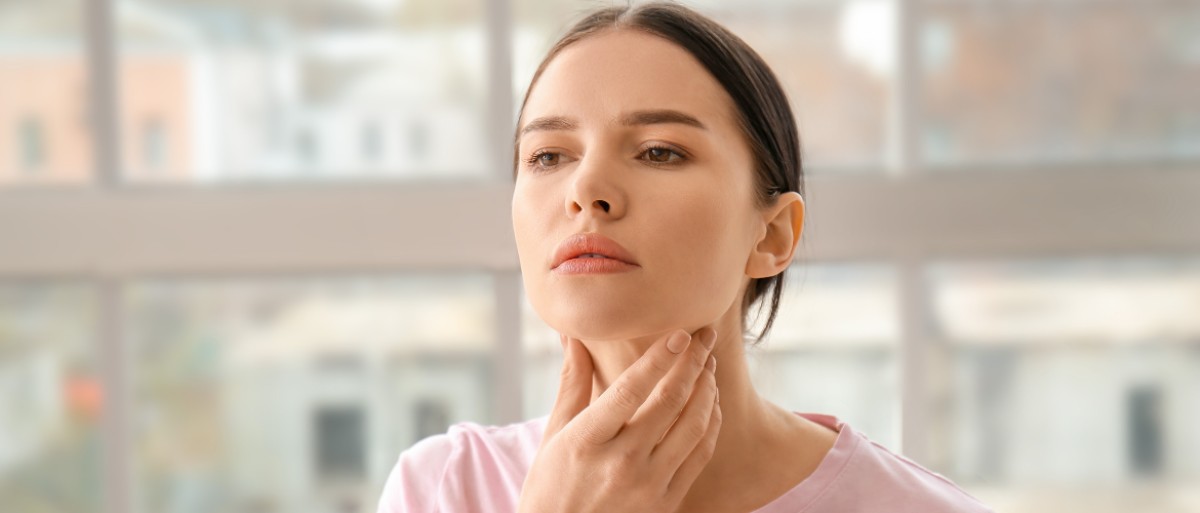
streptococcus is a bacterial infection that belongs to the category of Streptococcus pyogenes, or otherwise group A streptococcus. He is known for
severe pain in the neck which causes, and while it is
more common in children, can also affect adults.
How It Manifests
The
main signs of infection include:
- Sudden sore throat
- Difficulty and pain when swallowing.
- Red and swollen tonsils, sometimes with white spots or streaks of pus.
- Fever and headache.
- Motion sickness or vomiting, especially in children.
Symptoms of Streptococcus
The
symptoms of strep they may be considered alarming and require an immediate visit to the doctor. Let's look at some important signs to look out for:
- Sore throat that lasts more than two days: If the sore throat continues for more than 48 hours, it may be a sign of strep.
- Fever: Fever in children above 38,5°C.
- Sore Throat With Rash or Breathing Problems: The presence of a rash or difficulty breathing along with a sore throat may indicate a more serious condition.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: A sore throat accompanied by swollen lymph nodes is also a cause for concern.
- Lack of Improvement after Antibiotic Treatment: If strep is diagnosed and there is no improvement after 48 hours of antibiotic treatment, this requires a visit to the doctor
Treatment and Prevention of Streptococcus
Η
treatment and prevention of strep require concerted efforts, including medication and changes in daily routine:
Antibiotic Education
- Diagnosis: The diagnosis is made with a "strep test", a simple procedure that detects the presence of the bacterium.
- Antibiotics: They are usually prescribed by the doctor after the diagnosis. If taken within 48 hours of the onset of illness, they reduce the duration and severity of symptoms, the risk of complications and the chance of transmission to others.
- Symptoms: With treatment, improvement usually occurs within a day or two. In case there is no improvement after 48 hours of antibiotic treatment, it is recommended to contact the doctor.
- Full Treatment: It is critical to complete the course of antibiotic treatment to avoid relapses and serious complications, such as rheumatic fever or inflammation of the kidneys;.
Relief of Symptoms
- Analgesics: It is important to use pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen to relieve sore throat and reduce fever.
- Home Care: much rest, hydration with plenty of water, eating easily digestible foods such as soups and purees, and avoiding irritants such as smoking.
- Gargle with Salt: Gargle with warm salt water to relieve sore throat.
- Honey: It can also be used to relieve a sore throat (not recommended for children under 12 months).
Steps to reduce the risk of infection and spread of the bacteria.
- Rich Sleep: Sleep helps the body fight the infection. If you have strep symptoms, prefer to stay at home.
- Hydration: Drink enough water. Water helps keep the throat hydrated and makes swallowing easier.
- Consumption of Soft Foods: Choose foods that are easy to swallow such as broths, soups, mashed potatoes, soft fruit, yogurt and soft-boiled eggs.
- Gargle with Warm Salt Water: Especially for older children and adults, gargles help relieve sore throats.
- Honey: Honey can be used to relieve it sore throat. Do not give honey to children under 12 months.
- Avoiding Irritants: Smoking and other irritants, such as vapors from paints or cleaning agents, can irritate the throat and increase the risk of infections.
- Frequent hand washing.
- Covering the mouth elbow or tissue when coughing or sneezing.
- Avoid sharing personal items, such as glasses or cutlery.
These tips can help
prevention and relief of symptoms of infection by
streptococcus.
Η
Streptococcus transmission occurs through multiple pathways, often requiring close contact with individuals who already carry the microorganism. The following are clarifications regarding the main sources of transmission:
- Close Contact with Infected Persons: Ο streptococcus it can be spread from people who are already infected, through physical contact or even through breathing in the same space.
- Contaminated Droplets and Excreta: Coughing, sneezing, or other secretions from infected individuals are an important source of dispersal of the microorganism.
- Surfaces With Microbial Traces: Ο streptococcus it can survive for a period on various surfaces, such as handles, tables or other objects that are frequently touched by the hands.
- Skin Damage Caused by the Microorganism: In cases where the streptococcus causes skin diseases, these lesions can be a source of transmission.
- Healthy Carriers of the Microorganism: Although less common, there is the possibility of transmission from people who do not show symptoms but carry the microorganism.
Understanding these routes of transmission is important to avoid exposure to
streptococcus and ensuring health.
Knowing about and treating strep early can minimize the effects and provide relief from symptoms. Do not ignore early signs and contact your doctor for guidance and advice.
Find on
wecare.gr the right vitamins you need!
Sources: 1)
Strep throat - Symptoms & causes, 2)
Strep Throat: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment, 3)
What is strep throat?, 4)
Strep Throat Symptoms
PHARMACIST, M.Sc.
CEO Wecare IKE
Liability Disclaimer
The content of this website does not constitute and cannot be construed as medical advice, diagnosis, treatment or suggestion.
All information is provided to readers by healthcare professionals for informational purposes only. This content is not intended to be a substitute for personalized medical advice, diagnosis, prognosis or treatment.