Free shipping on orders over 39.00€
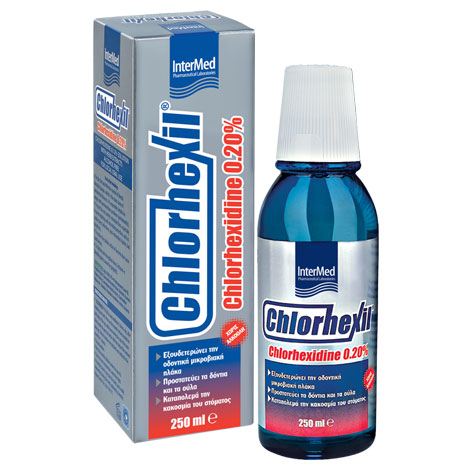
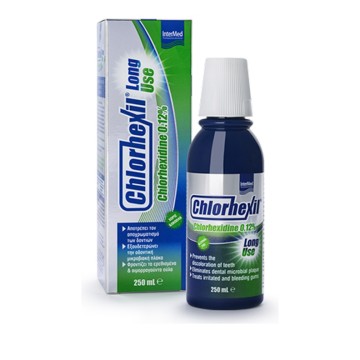
Intermed Chlorhexil 0.20% Oral Solution 250ml
Antimicrobial protection
The Chlorhexil 0,20% Mouthwash with a chlorhexidine content of 0.20%, was created for the active control and neutralization of the microorganisms of the oral-pharyngeal cavity, the effective control of the gingival microbial plaque and the immediate relief and protection of the oral cavity from irritations and periodontitis (in cases of inflammation) pharyngitis, tonsillitis, etc.
INDICATIONS
• Treatment of periodontitis
• Patients with immunosuppression or inability to perform a cleansing mechanism
• In the treatment & relief of the symptoms of a pharyngitis or tonsillitis (gargling)
With chlorhexidine 0,20%, chamomile extracts and α-bisabolol.
Without the presence of alcohol. With a wonderful taste of herbs.
Fl. 250 ml
User Manual
Rinse your mouth for 30-60sec with 10ml of undiluted CHLORHEXIL 0.20% solution, 2 times a day, for 5 to 7 days.
RELEVANT ARTICLES
Gingivitis
The term gingivitis describes the pathological condition that concerns the gums and is characterized by symptoms of inflammation and bleeding. Inflamed gums appear swollen, red and tender and may bleed either spontaneously or during brushing or flossing. At the same time, sensitivity or pain of the teeth may be observed during chewing and malodor of the oral cavity, while as this condition turns into periodontitis, the mobility of the teeth increases, thus leading to their loss.
The main cause of the appearance of gingivitis is the irritating presence of dental microbial plaque and the undisturbed action of pathogenic microorganisms, which find shelter under the protective layer created by the microbial plaque, which slowly turns into resistant tartar (or tartar). due to its calcification. A consequence of the formation and concentration of the stone is the loss of the support of the teeth.
As the gums gradually pull away from the teeth, the root of the tooth is exposed and the bone that holds the tooth in place is destroyed, causing the tooth to become more mobile than normal and eventually be lost, often without showing any signs of decay. damage to its surface.
In this early stage of gingivitis, the damage can be reversed with proper oral hygiene as permanent damage to the connective tissues or bone has not yet occurred. Otherwise, this situation progresses and leads to the appearance of periodontitis and irreversible damage.
"This information is intended for general information and information to the public and is in no way a substitute for the advice of a physician or other competent health professional."
Dental microbial plaque
Dental plaque is a sticky clear or whitish or yellowish coating that forms on tooth surfaces when they are not brushed or brushed incorrectly. Components that make up O.M.P are: microbes, food residues and various components of saliva. The only and most appropriate way to prevent O.M.P. is daily proper brushing.
Correct brushing includes cleaning all three surfaces of the tooth (buccal-maxillary-mastural) as well as the interdental spaces with dental floss or even interdental brushes in pathogenic situations. A simple way to verify the effective removal of O.M.P is the use after brushing of fuchsin solution to stain the residual microbial plaque.
O.M.P is characterized in sub-gingival and supra-gingival.
If plaque is not removed within 24-28 hours it begins to harden and form a hard deposit called tartar or tartar. So tartar is a hard calcified substance that is attached to the teeth and is formed from the plaque and from salts present in the saliva. Tartar cannot be removed by brushing but only by the process of scaling (teeth cleaning) by the dentist. Subgingival tartar that develops below the gum line makes it more difficult to remove the plaque film and can lead to chronic inflammation and periodontal disease. For this reason, it is recommended for all patients, healthy and not, a standard dental checkup every 6 months.
"This information is intended for general information and information to the public and is in no way a substitute for the advice of a physician or other competent health professional."
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a development of gingivitis and unfortunately leads to irreversible damage to the surrounding tissues of the teeth while it seems to be the most common cause of their loss in adults.
Predisposing factors for its appearance, in addition to stone formation, are smoking, uncontrolled diabetes, stress, reduced response of the immune system, poor diet, grinding of teeth, orthodontic abnormalities, hormonal changes, the taking of various preparations (such as contraceptives, antiepileptics, etc.) while 30% of the population is considered to have a genetic predisposition.
To detect periodontal problems, the dentist examines your gums. For this purpose he uses a tool called periodontal apples and locates the so-called pockets between the gums and the teeth. At the end of the gum line the gums do not attach to every tooth. There is a very shallow V-shaped groove between the tooth and the gum called the gingival groove. If the depth of the groove is greater than or equal to 3mm then the patient should start treatment immediately.
In periodontal patients, plaque bacteria begin to penetrate between the teeth and gums, where the environment favors the growth of anaerobic microbes below the gum surface. Periodontal pockets begin to form below the gum line.
The connective tissue and bone surrounding the tooth becomes infected. Bacterial toxins, as well as the immune system's defense enzymes that fight infection, begin to destroy the periodontal tissues that hold the teeth in place.
As periodontitis progresses, the periodontal pockets deepen and an ever greater mass of connective tissue and bone is destroyed. Periodontitis treatment must now be done by a specialist periodontist.
Teeth are constantly loosening, and without immediate periodontal treatment, one or more teeth will be lost (either on their own or because they will have to be extracted by the dentist to treat infection).
The daily and correct hygienic care of the teeth and gums with products that effectively fight pathogenic microorganisms and prevent the appearance of plaque, tartar and gingivitis as well as lifestyle changes and the regulation of coexisting pathological conditions are the only measure for prevention and the treatment of gingivitis and periodontitis.
"This information is intended for general information and information to the public and is in no way a substitute for the advice of a physician or other competent health professional."
EAN: 5205152000303, 5205152017844