Free shipping on orders over 39.00€
Natures Plus Ultra Omega 3/6/9 60 Softgels
FATTY ACIDS
Fatty Acids are distinguished into Saturated Fatty Acids (Saturated Fatty Acids) and Unsaturated Fatty Acids (Unsaturated Fatty Acids). The former have single bonds between carbon atoms (CC), while the latter have one or more double bonds (C=C).
Saturated fatty acids are recommended not to represent more than 11% of total daily calories, because they increase cholesterol and the risks of heart disease and many other diseases, including diabetes and cancer.
In general, animal fats are high in saturated fatty acids and low in unsaturated, while the opposite is true for fish and vegetable oils, with some exceptions, such as coconut oil and palm oil.
In the food industry it is very common to convert unsaturated oils (unsaturated fatty acids) into solid and semi-solid cooking fats and margarines, by adding hydrogen to the unsaturated (double) bonds. The process is called hydrogenation, and hydrogenated fats have properties similar to those of saturated fats (saturated fatty acids). Given the harmfulness of hydrogenated fats, which has been proven by specialized studies, it is an act of prudence to avoid, if possible, foods that contain the term "hydrogenated" in their ingredients. Of course, this is not possible with foods that are sold in bulk, such as pastries and pies.
Unsaturated Fatty Acids, which do not increase cholesterol and have a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system, are classified as Monounsaturated Fatty Acids with a carbon double bond and at Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids with two or more carbon double bonds.
Monounsaturated fatty acids are mainly represented by oleic acid (Omega-9), which makes up 72% of the fatty acids of the olive, and is also the fatty acid with the greatest distribution in nature. Research has shown that it is beneficial for the heart, while it may also have anti-cancer properties.
Of the polyunsaturated fatty acids, the group of Omega 3 and their team Omega 6 fatty acids.
OMEGA FATTY ACIDS (Omega-3 and Omega-6)
Alpha Linolenic Acid (ALA) from the Omega-3 group and Linoleic Acid (LA) from the Omega-6 group are called necessary (essential), because they cannot be produced by the body, but must be obtained from food (as is the case with vitamins and minerals).
Note:
In popular medical and dietary publications, all omega fatty acids, especially EPA and DHA, are often referred to as "essential". This, of course, according to the scientific definition of "nutritionally necessary", is not correct, despite the importance of EPA and DHA, and despite the fact that they are largely obtained directly from food or that they can treat some (but not all) ) from the symptoms of essential fatty acid deficiency.
Non-essential fatty acids can be produced from the two aforementioned essential fatty acids ALA and LA and/or obtained from food, according to the following simplified scheme:
*Despite the excellent usefulness of omega-3 fatty acids, we must take into account that oily fish, if they come from seas polluted with urban, industrial or other pollutants, may contain high concentrations of toxic substances, such as insecticides or highly toxic heavy metals (mercury, lead, cadmium, etc.). Nature's Plus, due to the multi-testing system it applies in its state-of-the-art laboratories, as well as its adoption of California's draconian Proposition 65 on toxic substances, is able to offer omega-3 fatty acids completely free of heavy metals or other toxic substance. On top of that, there's always the independent lab guarantee, since Nature's Plus is the only company that involves an independent FDA-jurisdiction lab in its product testing process (thus making it legally responsible).
It should also be noted that the product of Nature's Plus Metal Control it is excellent for detoxification, in general, and for heavy metal detoxification, in particular (see related leaflet).
OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS (EPA and DHA)
Fish oils and fatty fish such as salmon, tuna, sardines and mackerel are the best dietary sources of the important fatty acids EPA and DHA.
Also, a number of vegetable oils, especially flaxseed oil, are rich in Alpha Linolenic acid, which is a structural component of cell membranes and can be converted in our body into EPA and DHA.
These important fatty acids of the omega-3 series have, among others, the following properties:
PROPERTIES EPA and DΕA
- They are particularly beneficial for the health of the cardiovascular system.
- They reduce the level of triglycerides, which is especially good for the heart, since, after all, triglycerides are a greater risk for heart disease than cholesterol. According to a recent study (Amer J Clin Nutrition, Jul 2002) liver oil supplements containing EPA and DHA lower triglycerides and blood pressure and make blood vessels more elastic.
- They reduce the tendency of blood platelets to stick together, thus acting preventively against the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- There is some evidence that they reduce the chances of sudden death in patients who have had a heart attack. Some researchers express the opinion that a daily intake of less than 1.000 mg of EPA+DHA is enough to save 20 out of a thousand heart attacks.
- They relieve some symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis and help prevent relapses of Crohn's disease. Treatment for the above cases should last for at least 10-12 weeks.
- In vitro and animal studies have shown that they reduce tumor formation, inhibit cancer growth, enhance apoptosis and programmed cell death, and have anti-angiogenic activity.
So far only one preliminary study in humans has been done, which gave positive results in breast cancer. Of course, other studies are needed in order to draw safer conclusions.
EPA and DHA also help cancer patients reduce or stop the loss of muscle mass, which is of particular importance given the nature of the disease.
- They can significantly help reduce hypertension, taken together with other appropriate supplements, such as magnesium, potassium, CoQ10, in the context of an antihypertensive diet.
- Because of their anti-inflammatory properties, they may reduce asthma attacks and protect heavy smokers from emphysema.
- They help prevent rejection of transplanted kidneys.
- There is evidence that they can help in cases of angina.
- Combined with GLA (Omega-6 fatty acid) they improve vitality and help patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. A related study lasting 3 months gave positive results in 85% of cases. The same combination (in a ratio of 1 EPA to 4 GLA) gave good results, both in limiting kidney stone formation and in limiting hypercalciuria (J Urol, 1993, 149:253A).
- There appears to be a link between Omega-3 fatty acids and mental health in general, and depression in particular, which is not surprising considering that over 50% of our brain cells are made up of fat cells.
In an article in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Joseph Hibbeln and Norman Salem of the US National Institutes of Health linked the ever-increasing cases of depression over the last 100 years in North America to the ever-decreasing intake of Omega-3s over the same period. .
The same scientists, on the other hand, discovered that residents of coastal areas, where fish consumption is high, suffer from depression much less than residents of inland areas, where fish consumption is low.
Low levels of DHA have also been associated with senile dementia and Alzheimer's, with memory loss and with vision problems (DHA concentration is high in the brain's gray matter and retina).
A study of elderly Alzheimer's patients in Sweden was found to have low levels of DHA in the blood, while studies in Japan showed a significant improvement in the symptoms of senile dementia in patients given DHA supplements.
Finally, the results of a recent study are interesting, according to which babies whose nursing mothers had higher levels of omega-3s were calmer, had more restful sleep and had less sleepiness immediately after waking (Amer J Clin Nutr , 2002, 76:608-13).
- EPA and DHA help to achieve better sports performance, due to their anti-inflammatory effect and the reduction of blood coagulability, resulting in a better supply of tissues with oxygen and nutrients.
Moreover, according to some testimonies of athletes and physical therapists (mainly from Denmark), omega-3, in combination with borage oil (omega-6), vitamins A, B-6, C, E, and the minerals selenium and zinc, are effective for repetitive inflammatory joint injuries known as "tennis hand" and "golfer's hand".
Results are visible within 2-3 weeks, while more severe cases require more time.
- They seem to be effective against dysmenorrhea. In a study done on teenage girls, EPA, DHA and vitamin E were given. After two months period pain was significantly reduced (Amer J Obst Gyn, 1996, 174:1335-1338).
- There is strong evidence that both EPA and DHA, as well as omega-6 fatty acids (linoleic acid, GLA), help patients with multiple sclerosis by prolonging periods of remission and reducing the number and intensity of attacks (Neurology, 1984, 34:1441-5).
REMARKS
- Many of the studies that have been done to investigate the properties of EPA and DHA have used high dosages (over 2500 or over 5.000 mg). This is not always easy in everyday practice.
The best solution would be, perhaps, the parallel increase in fish consumption (preferably fatty) or the use of flaxseed oil or whole flax seeds. Flaxseed oil is an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids.
Linseed oil can also be used in salads, but never in cooking, because it is destroyed by high temperatures. Also, it should always be in dark, hermetically sealed bottles, because it oxidizes very easily. Make sure you are buying from a company that takes great care in the quality of its products. The airtight capsules (softgels), however, protect the linseed oil better.
- Products containing EPA and DHA should also contain vitamin E to protect against oxidation. People who live in a polluted environment or smoke a lot or have a poor diet (fast food, ready meals) should take these products with additional vitamin E or with antioxidant products, to protect EPA and DHA from oxidation in the body. These people, anyway, generally need antioxidant protection.
- Codfish oil usually contains appreciable, but not high, amounts of EPA & DHA. If you increase your intake too much to get more EPA and DHA you risk the toxicity of vitamin A, which is contained in a large amount in cod liver oil, is not excreted in the urine (it is fat soluble) and is toxic in high doses.
CONTRAINDICATIONS - PRECAUTIONS
EPA and DHA and Alpha Linolenic Acid have no toxicity.
Because of their antithrombotic properties, they should be taken with caution by hemophiliacs and those taking antithrombotic drugs, and should be discontinued before an operation.
Children who have frequent nosebleeds should limit their consumption of cod liver oil or other fish oils.
ΩMEGA-6 FATTY ACIDS
The group of omega-6 fatty acids is also extremely important for the proper functioning of our body. Two of the acids in the group are the most important: Linoleic acid, which is essential - so it cannot be synthesized in our body and must be obtained from food - and Gamma Linolenic Acid (GLA), the which has great therapeutic value.
But we should point out that, although linoleic acid is so important that its complete lack would cause the death of our cells, its overconsumption can also cause health problems.
Indeed linoleic acid, which has certain inflammatory properties, competes for the same enzyme-converter as alpha linolenic acid which has anti-inflammatory properties (the former can be converted in our body into omega-6 and the latter into omega-3 fatty acids) .
Thus, an overconsumption of linoleic acid can cause symptoms of EPA and DHA deficiency if our diet is poor in these valuable fatty acids and our body relies on alpha linolenic acid for their synthesis.
According to the estimates of expert scientists, the ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids in the diet of the inhabitants of developed Western countries is today of the order of 1 to 24, while when man lived as a hunter and fruit gatherer it was of the order of 1 to 5.
If we take into account that the human body remains basically unchanged from prehistoric times to the present day, then this great nutritional upheaval can explain the epidemic proportions that heart disease, cancer, diabetes and other degenerative - and not only- diseases.
Of course, the other nutritional upheavals have contributed equally, if not more, in this direction: the great increase in the consumption of saturated fats, the processing of food and stripping it of vital components (vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, etc.) and the skyrocketing of refined carbohydrates (starches, simple sugars), with a parallel skyrocketing of fiber.
Fortunately for our country, the problem of overconsumption of linoleic acid does not seem to exist for the great majority of the population, due to the extensive use of olive oil, which contains mainly oleic acid (omega-9).
In contrast, seed oils, which are widely consumed in other Western countries (mainly sunflower oil, corn oil, soybean oil), are very rich in linoleic acid. In addition, these oils are almost always refined, which means that almost all of their valuable components have been destroyed, and they also contain residues of the chemicals used in refining.
In conclusion, due to the wide spread of linoleic acid in our dietary sources, combined with the widespread use of olive oil, problems of both insufficient intake and overconsumption do not seem to be common in our country.
(For GLA, the most important omega-6 fatty acid, see below, product ULTRA EPO 1.500).
EAN: 097467039674
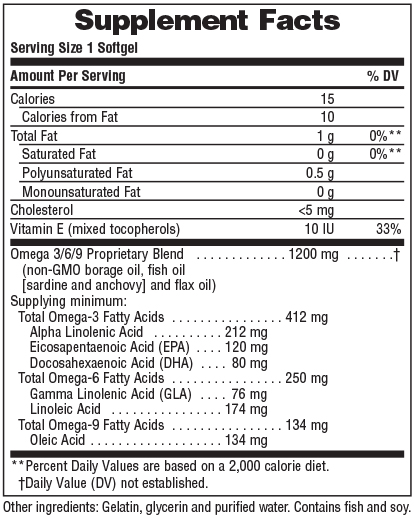
Components
Use
Common use: One capsule twice a day.